Data is the engine that drives modern business.
Every day, your company collects a lot of information, such as customer contacts and interactions, sales activities, orders, quotes, warehouse inventory, logistics, support tickets, and marketing campaign data.
But, do modern businesses use this wealth of collected data? Unfortunately, statistics show that they don’t.
- Around 68% of collected enterprise data goes unused. Source: Seagate and IDC.
- Up to 73% of company data goes unanalyzed. Source: Inc. and Forrester.
- Around 97% of organizations faced data quality challenges in their digital transformation efforts. Source: Gartner.
- Poor data quality costs businesses in the US alone about $3.1 trillion annually. Source: IBM.
Often, companies gather data from diverse sources. Moving data from one source to the other in order to get a unified view of the information can be difficult. As a result, many end up having disconnected systems and silos of data.
One of the most effective solutions to this challenge is real-time data integration. Especially if you’re using multiple SaaS applications. To connect siloed data, you need a smart approach to data management, aka a solid integration strategy.
In this article, we will investigate the different data integration methods to help you choose the right solution that will help you get those actionable insights into your business growth.
WHAT IS DATA INTEGRATION
Data integration is the process of combining data from many different data sources, typically for analysis, business intelligence, reporting, or loading into an application.
It’s like cooking: you take various ingredients (your data) and use different data integration methods to create a meal (practical business insights).
Businesses often use a lot of applications to improve efficiency and serve their customers better. And, most of the time, these applications have their own databases and data warehouses.
Yet, if they are separated and unconnected, they bring little benefit. Therefore, for them to work together, they need to communicate! So, data integration is a must, as it creates a unified view of all data assets.
EXAMPLE
An e-commerce company decides to connect its CRM and ERP systems.
When a customer places an order, secure data transfer ensures that both systems instantly share information: the CRM tracks the customer's purchase history and preferences, and the ERP manages inventory and shipping.
Connecting these systems allows the company to notice such trends as: which products certain customer groups buy more often, or when they typically make purchases. This information then helps personalize marketing communication and plan inventory better – all because these two systems are talking to each other.
HOW TO GET THE MOST OUT OF DATA INTEGRATION
Every day businesses use a lot of applications, systems, and data warehouses. For these systems to work in unison, they need to be connected, because otherwise it becomes nearly impossible to make better sense of all the available information.
Put simply, all data must be available in a single place, in real-time for all the right stakeholders (including manufacturers, suppliers, logistics companies, customers). This way you’d be able to optimize processes and improve customer service.
To illustrate the tangible benefits of data integration, let’s continue with the ERP-CRM integration.
Businesses put a lot of effort into making every prospect or customer satisfied. They want to know all about their customers’ needs and requirements. That’s why turning this vendor-customer relationship into a partnership is the most efficient sales approach.
And from the operational standpoint, the benefits of such integration are plenty:
- Panoramic view of the customer. A CRM system can significantly enhance your understanding of your customers. However, for an accurate 360-degree view of your customer, integrating your CRM with your ERP is essential.
From prospecting to sales and support, to finance and accounting, together, these systems provide complete visibility into your customers’ needs, buying habits, order history, preferences, account standing, etc.
- Improved operational efficiency. Instant access to critical information in real-time (whichever system you are working in) means that you can quickly and accurately respond to your customers’ and other stakeholders’ questions and requests.
Getting information about inventory levels, shipments, customer financials, order history, returns, payments, pricing, etc., without having to search for answers in multiple systems is a time-saving game-changer.
- Elimination of manual work. Getting rid of time-consuming, manual routines that are prone to human error is a must for companies that want to grow. Data integration helps eliminate redundant data entry, simplify processes, automate workflows, and even shorten customer support’s response time.
It results in less time shuffling between screens, happier customers, and staff who can focus on more important work than copying and pasting data
A CRM system can significantly enhance your understanding of your customers. However, for a comprehensive and accurate 360-degree view of your customer, integrating your CRM with your ERP is essential.
EXAMPLE
An online furniture company was struggling to keep up with 500+ orders per month.
The team spent hours manually copying order details from their e-commerce platform, accounting software, and shipping system. Customer support reps had to juggle between three different screens just to answer a basic "Where's my order?" question.
After implementing data integration, the company connected all these systems to work as one.
Now, when a customer orders a sofa, the information automatically flows everywhere it needs to go. The warehouse gets instant picking lists, the shipping system creates labels automatically, and the accounting software updates in real-time. What used to take 15 minutes of data entry per order now happens in seconds.
TYPES OF DATA INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES
Deciding how to perform a data integration project can be a difficult decision to make. It requires a good understanding of what data integration methods and techniques are and which ones fit your business best.
There are many types of data integration, and you can easily get lost in readings about data migration, data streaming, data models, data virtualization, or data federation. Therefore, it’s important to keep it simple.
The most common data integration techniques can be grouped into five categories:

1. UNIFORM DATA ACCESS
With Uniform Data Access, you can access enterprise data from disparate sets and present it uniformly, while allowing the data to stay in its original location.
The Uniform Data Access provides one standard method to access data, regardless of where it's stored in databases, files, cloud services, etc. It handles all the complex stuff behind the scenes, such as different data formats and storage systems. It also lets applications work with data without needing to know the technical details of how or where it's stored.
In other words – you don't need to know how each system works - you just ask for what you want, and the Uniform Data Access layer figures out the "how" part.
The benefits of the Uniform Data access data integration techniques include:
- Simpler application code,
- Easier maintenance,
- Reduced training needs,
- Flexibility to change data sources without changing application code,
- Consistent data handling across the organization.
But Uniform Data Access has limitations. You can only use this integration method on similar data sources (same type of database). Also, data management only allows you to have limited information about the data's history and version management.
➡️ For example, an e-commerce company that needs to retrieve customer information from its SQL database, a cloud storage service, and a CRM system can use a single set of commands to access all the customer data, without needing to know the technical details of each system.
2. COMMON DATA STORAGE
Common Data Storage (or CDS) is a data integration approach where data from different sources is copied and stored in one central location, using one standard format.
Also known as Data Warehouse, CDS includes data version management and allows you to combine data from different sources, such as mainframes, databases, flat files, etc.
The benefits of CDS include:
- single source of truth for all data,
- consistent data format,
- simpler data access (one place to look),
- better performance (no need to fetch from multiple sources),
- easier backup and security management,
- historical data preservation.
As to the limitations of this data integration technique, you should be aware that data might not be real-time (it depends on update frequency), CDS requires more storage space (for storing copies), you’ll need to maintain synchronization with source systems, and may face scalability challenges with very large datasets.
➡️ For example, a retail company copying daily sales data from all stores into a central data warehouse. Instead of querying each store's system separately, analysts can access all sales data from one place, in one format.
3. Application-Based Integration
Application-based Integration is a method of connecting different software applications that a company works with by using a central app or platform to manage data flow between them.
Instead of each app storing and processing data separately, an integration tool pulls data from various sources, processes it, and sends it to the correct applications. This data integration technique allows a business to combine information from multiple tools without having to modify each one individually.
The benefits of the Application-based Integration are:
- it helps maintain data consistency, improving accuracy across apps,
- it simplifies data management by reducing the need for manual updates,
- It prevents duplicate data entry.
But, the Application-based Integration has limitations, especially if you are handling large volumes of data and large numbers of sources. Therefore, this technique is mainly suited to integrate a minimal number of applications and for more limited amounts of data from a limited number of sources and applications.
➡️ For example, a customer support app can instantly access updated customer data from a CRM system through an integration platform, making service faster and more personalized.
4. MANUAL DATA INTEGRATION
Also known as common user interface, Manual Data Integration is an approach where users access multiple data sources through a single interface (like a dashboard or a portal), but the data stays in its original locations and formats.
In other words, it simply presents the different data sources in one view and lets users see these multiple sources at once, while the original data is kept in its original location.
The benefits of the Manual Data Integration technique are:
- it’s simple, quick to implement, and no complex data transformation needed,
- data remains up-to-date (real-time access),
- lower initial cost.
On the flip side, the limitations are plenty. This technique requires manual effort to combine/analyze data, and as a result is prone to human errors. Moreover, it’s time-consuming, especially for large datasets, and may end up having inconsistent data formats between sources, and can only be used with a minimal number of sources and a small volume of data. And there are little automation possibilities.
➡️ For example, a financial analyst uses a dashboard that displays both QuickBooks accounting data and Salesforce customer information side by side, but must manually copy and combine the data in Excel for analysis.
5. Middleware Data Integration
Middleware is a layer of software that creates a common platform for all interactions internal and external to the organization:
- system-to-system
- system-to-database
- human-to-system
- web-based interactions
- mobile-device-based interactions
Acting as an intermediary layer that handles data movement and transformation, Middleware Data Integration connects different systems and applications, translates data between different formats, routes information between systems, manages data transformations in real-time, and handles security and access control.
Middleware technology has helped many companies rationalize legacy IT systems into reusable, general-purpose functionality blocks that facilitate quicker changes to business processes.
Many middleware services are accessed through APIs – sets of tools, definitions, and protocols that allow applications to communicate with each other. APIs make it possible to connect completely different products and services through a common layer.
As to the limitations of the Middleware data integration technique:
- it can be expensive to implement,
- it adds another layer of complexity and requires specialized expertise,
- it needs ongoing maintenance and can be challenging to troubleshoot,
➡️ For example, a hospital uses middleware to automatically translate and transfer patient records between its appointment scheduling system, electronic health records, and billing system, ensuring all systems stay synchronized in real-time.
BUSINESS BENEFITS OF DATA INTEGRATION FOR SAAS
SaaS companies can benefit a lot from data integration by unifying all their data sources.
Instead of scattered data repositories, data integration gives them a centralized view of their operations and customer interactions. This leads to better decisions that are based on real data, not guesses, and reduces duplicate data entry and manual work.
Business leaders can quickly spot opportunities, issues and trends, while customer support teams can improve their service by having immediate access to all relevant customer information.
Moreover, data integration speeds up innovation for SaaS companies. When data flows smoothly between applications, teams can experiment, test, and release new features more effectively – because they have complete information at hand.
Finally, data integration improves security and compliance, as it ensures all data is stored and managed consistently, reducing the risk of errors or security breaches.

EXAMPLE
A project management software (SaaS) company had its customer data stored in too many places. Their support team used a help desk system, their customer success team worked in a separate customer portal, and their usage data was sitting in yet another analytics tool. There was no way to quickly find out what their customers were up to.
By embracing real-time data integration tools, the company managed to connect all these systems. Now, when a customer contacts support, the team instantly sees a complete picture: recent feature usage, subscription status, past conversations, and even which training materials the customer has accessed.
More so, when a customer reported a workflow issue, the support team immediately saw the customer hadn't used a key feature that would solve their problem. Instead of just fixing the issue, the support team offered a personalized training session. Result? The customer learned about features they didn't know existed, their usage doubled, and they became one of the company’s advocates. Win-win!
WHICH DATA INTEGRATION TECHNIQUE SHOULD YOU SELECT?
All data integration techniques allow you to store, analyze, transfer, and view your data in a unified way.
To decide which technique suits your organization best and which data integration tool you should invest in, you need to fully understand your business and its processes. Also, you need to have a good understanding of the applications that your organization is using, as well as the reason why you are using them.
For example, if your needs are simple, then a relatively simple data migration tool will suffice. But if your needs are complex, then you might have to invest in a complex data integration platform.
Whichever data integration method you choose, to make it simpler, first of all, you need to ensure each application contains high data quality. Then, you need to evaluate the amount of data you have. If it’s substantial, then it’s advisable to seek professionals’ helps
Most large companies worldwide have invested in both an ERP system and a CRM system – some simultaneously, some step-wise.
A very common data integration scenario is that of an ERP-CRM integration. Most large companies worldwide have invested in both an ERP system and a CRM system, and integrating them is what can make the biggest difference to a company’s operations.
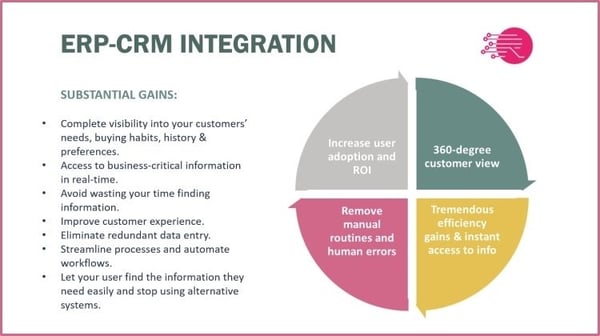
THE BENEFITS OF AN ERP-CRM INTEGRATION
- Complete visibility into your customers’ needs, buying habits, history, and preferences
- Access to business-critical information in real-time
- No more wasting your time looking for information
- Improved customer experience
- Elimination of redundant data entry
- Streamlined processes and automated workflows
- Easy ways to find the information you need – without using alternative systems
CHOOSING THE RIGHT DATA INTEGRATION TECHNIQUE
Finding the appropriate data integration method depends on factors such as data volume, real-time requirements, and security needs.
To help you choose the best integration technique for your business needs, you first need to consider these three factors:
- How quickly do you need the data?
- How much data are you handling?
- What resources (technical and budget) do you have?
Now, let’s visualize the five techniques we described above by who’s likely to benefit from each type most.
UNIFORM DATA ACCESS is best for the companies that:
- want to keep data in their original locations
- have strict data governance rules
- are financial institutions that can't move sensitive data
➡️ For example, a bank that needs to access customer data from multiple branches but regulations prevent data consolidation.
COMMON DATA STORAGE is best for companies that:
- need central data analysis
- want single source of truth
- have heavy reporting needs
➡️ For example, a retail chain consolidating sales data from all stores into a data warehouse.
APPLICATION-BASED INTEGRATION is best for:
- startups with limited resources
- companies with specific app-to-app needs
- organizations needing custom integration logic
➡️ For example, a small e-commerce company connecting their shopping cart directly to their inventory system.
MANUAL INTEGRATION is best for:
- very small businesses
- companies with infrequent data needs
- organizations with limited budget/technical resources
➡️ For example, a small consulting firm manually updating their client database weekly.
MIDDLEWARE DATA INTEGRATION is best for:
- large enterprises using many systems
- companies needing flexible connections
- businesses wanting pre-built connectors
➡️ For example, a marketing agency connecting multiple client platforms (social media, email, CRM)
Here is a quick checklist that should help you make the right decision.
|
Choose
|
When
|
|
UNIFORM DATA ACCESS
|
- Data must stay in place
- Real-time access is needed
- Security is paramount
|
|
COMMON DATA STORAGE
|
- Analytics is the primary goal
- Data consistency is crucial
- You’re willing to invest in infrastructure
|
|
APPLICATION-BASED INTEGRATION
|
- Specific apps need connecting
- You have development resources
- Need custom logic
|
|
MANUAL INTEGRATION
|
- Volume is low
- Frequency is low
- Budget is limited
|
|
MIDDLEWARE
|
- There are many systems to connect
- You need quick implementation
- There are pre-built, ready-to-use connections that someone else keeps updated and working
|
HOW DO RAPIDI DATA INTEGRATION SOLUTIONS WORK?
Rapidi was developed to make data integration projects as simple and robust as possible.
It is an innovative cloud integration system with pre-configured, adaptable business processes and templates that support the most common CRM-ERP integration points.
In particular, Rapidi’s data integration tool easily integrates Salesforce CRM application with any of the Microsoft Dynamics ERP solutions using pre-configured transfers/templates. Designed to enable direct integration, it makes your data flow easily between the two systems.
Installation is easy with the programming-free Rapidi data integration platform. No programming is required, even if you want to extend your Salesforce or Microsoft Dynamics with add-on solutions or customizations.
The underlying technologies in Rapidi contain specific features to optimize integration with Salesforce and Microsoft Dynamics ERP. As a result, you don’t even have to go through an extensive testing process. You just need to make sure you have good data quality.
Rapidi runs via the RapidiConnector, a unique technology that ensures data communication between Rapidi and your on-site systems is not compromised. The RapidiConnector resides in your network and is automatically compressed, and SSL encrypts data before transferring, making it practically impossible to decipher.
Rapidi Data Integration Solution is an innovative iPaaS integration hat is three-fold in its simplicity: in design, onboarding, and use. It is fast yet flexible, secure, and robust.
Key Takeaways
Data is crucial for modern business.
Yet still, a lot of companies are not using it effectively, as about 68% of enterprise data goes unused. This means only one thing – there is an urgent need for better data integration strategies.
There are five main ways to integrate data, each suited for different needs:
- Uniform Data Access is best for keeping data in place with real-time access.
- Common Data Storage is suitable for centralized analysis and reporting.
- Application-based Integration is great for connecting specific apps.
- Manual Integration suits small businesses with basic needs.
- Middleware is best for large companies using many systems.
When choosing a data integration technique, you should consider three fundamental questions: the speed at which you need access to data, the volume of data you’re handling, and your technical and budgetary resources.
A successful data integration is a godsend for any business – big or small. Not only will they get a comprehensive view of customers, reduce manual work, and improve their decision-making through real-time access to data, but they will also be able to enhance customer service and stay ahead of the emerging trends and customer behavior changes.
Transforming data into insights you act upon is the ultimate goal!
When choosing the right data integration technique for your business, remember – there's no one-size-fits-all solution. The best integration method depends on your specific business needs, resources, and goals. Success comes from matching the right method to your unique business circumstances.
So, choose wisely. Or better ask Rapidi for help! We will listen to your needs and offer the solution that fits your business goals.
Learn more
Follow us on LinkedIn to learn more about Rapidi Data Integration Solutions, and download this e-Book for additional information about Rapidi.

Frequently Asked Questions












